Magnolia 的内容个性化功能如何能助力您的业务
千人千面的数字体验
根据每个客户所属的受众类型、浏览方式等信息,为他们提供个性化的内容推荐。Magnolia 通过分析客户数据,让您为每个客户量身定制数字体验,从而提高他们的参与度、转化率和留存率。
为所有的数字交互渠道提供个性化的浏览体验
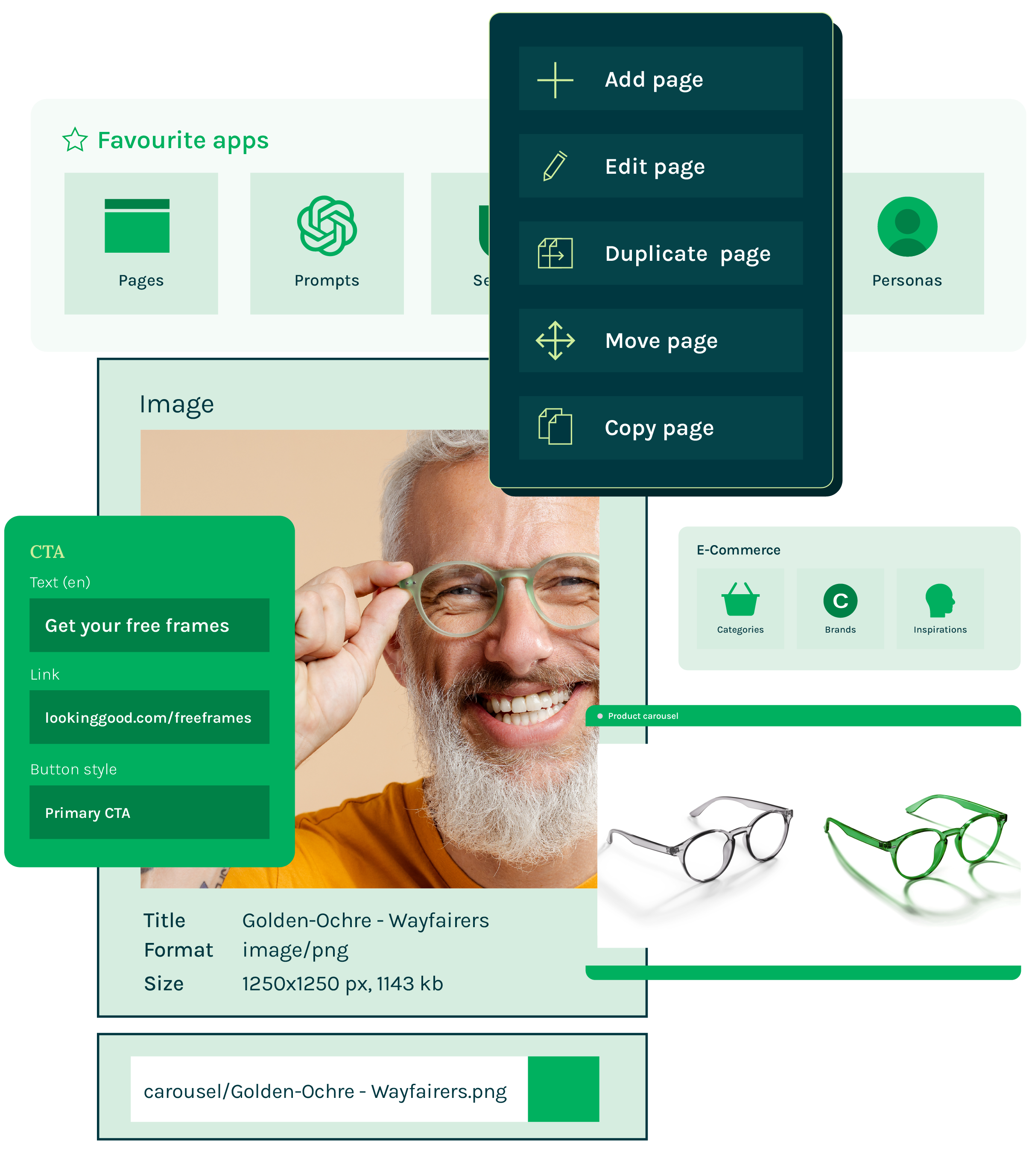
Magnolia 能帮您的企业实现全渠道内容的个性化和优化。通过 API 提供个性化的内容,从而在任何前端实现千人千面的浏览体验。
内容个性化、数据分析和内容优化
Magnolia 同时提供内容个性化和 A/B 测试功能,帮您打造卓越的数字体验,提高客户的长期价值。
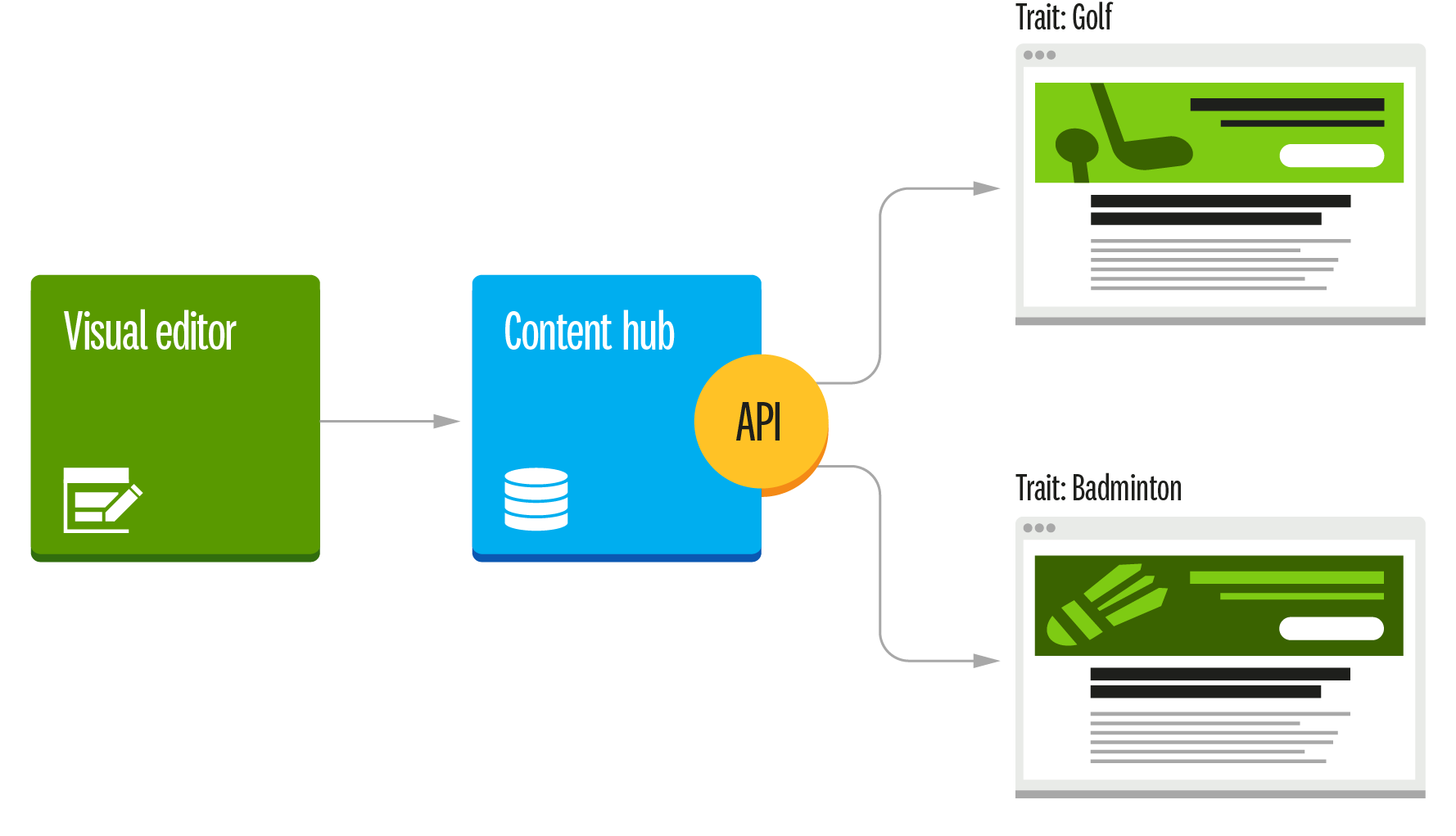
在所有数字交互渠道实现千人千面
前后端分离架构的灵活性使其越来越受欢迎,但是如何在前后端分离的架构中实现千人千面却成了难题。
Magnolia 可以帮您解决这个问题。您可以通过 Magnolia API 向任何前端提供个性化的内容。
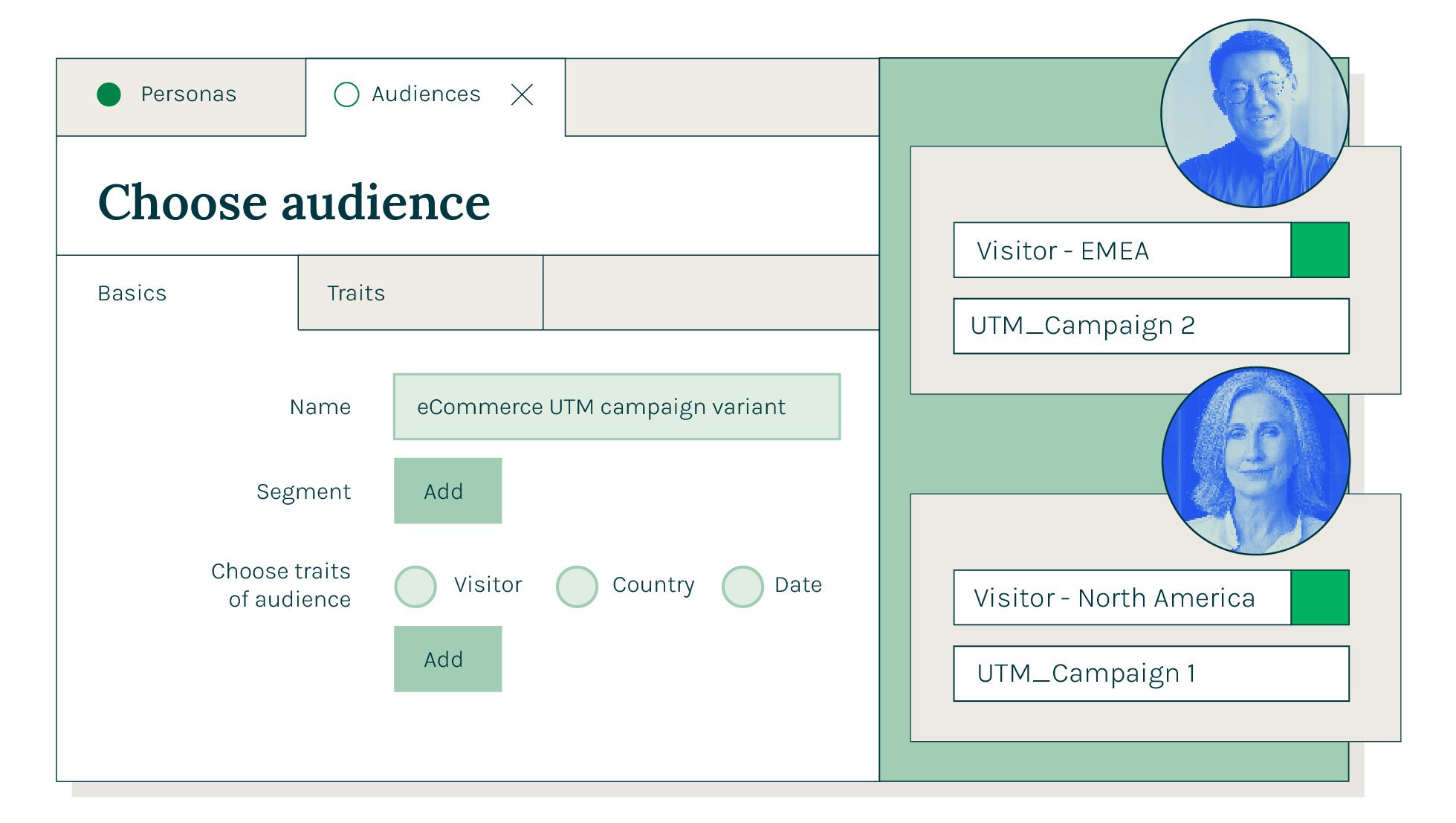
内容作者用 Magnolia 给每个的受众群体创建个性化的内容模块。IT 人员通过在他们的 API 请求中指定这些特征来索取个性化的内容,从而在前后端分离的架构中实现千人千面。











Guided product tour
See Magnolia Personalization in action
Create digital experiences that resonate with your target audience without touching any code.
扩展您的 MarTech 技术栈
受众群体
根据特定的受众特征定义受众群体并为每个群体打造个性化的数字体验,从而提高转化率和留存率。
A/B 测试
创建多个页面版本并通过 A/B 测试来找出最优解。
营销标签
在您的页面中插入跟踪和分析页面效果的代码,并整合来自社交媒体或广告网络的第三方内容。
统一客户数据
集成您的营销自动化工具以及CRM,以在系统内追踪用户行为,从而创建全面的客户画像。
数据分析
将您的分析仪表板直接引入 Magnolia 的创作界面,并在内容上下文中分析数据,帮助您改善数字体验。
搜索引擎优化
检查和审核内容,获取相关改善的建议,优化内容的 SEO 排名。

Optimization Integrations
All-in-one SEO, accessibility and content quality tools inside Magnolia - in one seamless workflow.
客户案例
通过我们的客户案例分析,了解我们的客户如何通过 Magnolia 平台来改善他们的客户数字体验并提高营收。